Free video consultation | Tuesday 24th February
The next session will be on
Tuesday 24th February 2026
With Dr. Martin Wiese
Book a free video consultation with one of our surgeons, to discuss your symptoms, explore treatment options, and receive expert advice, all from the comfort of your home.
Reclaim your active lifestyle with a natural, mesh-free bilateral hernia repair. Our techniques restore strength and mobility, helping you recover fully and get back to what you love most.
Choose our specialised approach to bilateral inguinal hernia surgery without the use of plastic meshes, prioritising your comfort, and supporting a fast, natural recovery.
98% success rate
Two weeks waiting list
6 weeks to full recovery
What is a bilateral inguinal hernia?
A bilateral inguinal hernia occurs when hernias develop on both sides of the groin. It involves the protrusion of organs or fatty tissue through weak spots in the abdominal wall. These hernias occur in the complex groin area, where muscles, tendons, vessels, nerves, and reproductive organs are located.
Bilateral inguinal hernias are less common than single-sided hernias, but they can have a more significant impact due to the involvement of both sides of the groin.

Symptoms
- A bulge in both sides of the groin that might disappear when you lie down.
- Pain or tenderness in both sides of the groin.
- Discomfort when lifting or straining.
- A burning or bubbling sensation in both groin areas.
- In some cases, bulges may extend into the scrotum.
What are your options for treatment?
If you’ve been diagnosed with a bilateral inguinal hernia, you might be wondering: Do I need surgery, or are there other ways to manage it?
The right approach depends on several factors, including the size of your hernia, your symptoms, and your lifestyle.
1. Surgical repair (The only long-term solution)
Since hernias cannot heal naturally, surgery is the only definitive way to repair the weakened area. There are two main surgical approaches:
- Mesh-Based Repair (Common in your local hospitals, but carries risks of chronic pain and foreign body reactions)
- Mesh-Free Repair (
 ) The natural alternative, reinforcing your own tissue without implants.
) The natural alternative, reinforcing your own tissue without implants.
At BioHernia, we specialise in mesh-free hernia repair because it provides a safer, more natural solution with less risk of chronic pain and complications. Our technique focuses on strengthening your natural tissue rather than relying on synthetic materials.
When is surgery recommended?
If your hernia is growing, causing pain, or affecting your daily activities, surgery is the best option to restore your comfort and prevent future complications.
Pros:
✅ The only definitive, long-term solution for hernias
✅ Prevents the hernia from growing larger or causing complications
✅ Restores strength to the abdominal wall
✅ Can relieve pain and discomfort caused by the hernia
✅ Different surgical options available (mesh-based or mesh-free)
Cons:
❌ Requires surgery and recovery time
❌ Some procedures (especially mesh-based) carry a risk of chronic pain or complications
❌ Potential risks include infection, nerve damage, or recurrence
❌ Temporary restrictions on physical activity during recovery
2. Watchful waiting (Non-surgical management)
For small hernias that cause no pain or discomfort, some people choose to monitor their condition rather than undergo immediate surgery. This is known as “watchful waiting.” However, hernias do not heal on their own—over time, they tend to grow larger and can become painful or even dangerous.
Pros:
✅ No immediate surgery required
✅ Suitable for small, symptom-free hernias
Cons:
❌ The hernia may grow and become more painful over time
❌ Risk of sudden complications like strangulation, which requires emergency surgery
3. Hernia belts or support garments
Some people try hernia belts or trusses to hold the bulge in place. While they may provide temporary relief, they do not fix the hernia and can even cause discomfort or skin irritation with prolonged use.
Pros:
✅ May reduce discomfort in certain situations
Cons:
❌ Does not treat the hernia—only masks symptoms
❌ Can weaken muscles over time, potentially making the hernia worse
The operation explained
Our mesh-free hernia repair technique directly addresses the issue by carefully stitching and reinforcing the weakened groin area, eliminating the need for plastic mesh. This method restores your natural tissue structure and is performed as out-patient surgery, meaning you’ll have the procedure and return to rest in the comfort of your own accommodation on the same day.
Bilateral hernia surgery
For bilateral hernia surgery, we carefully repair one side first before proceeding to the other during the same operation.
Start of the operation
After administering the anesthetics, we make a small horizontal incision of approximately 5 cm directly above your hernia, to access the hernia bulge.
Fixing your hernia
The hernia sac is gently reduced back into the abdomen and the weakness in your abdominal wall is closed with sutures, using either the Shouldice technique or the Desarda technique.
Closing the wound
Finally, the operation wound is closed using sutures and surgical glue. In all, the operation takes about 30 to 45 minutes to complete. After full recovery, a minor scar of 3 to 5cm is left.
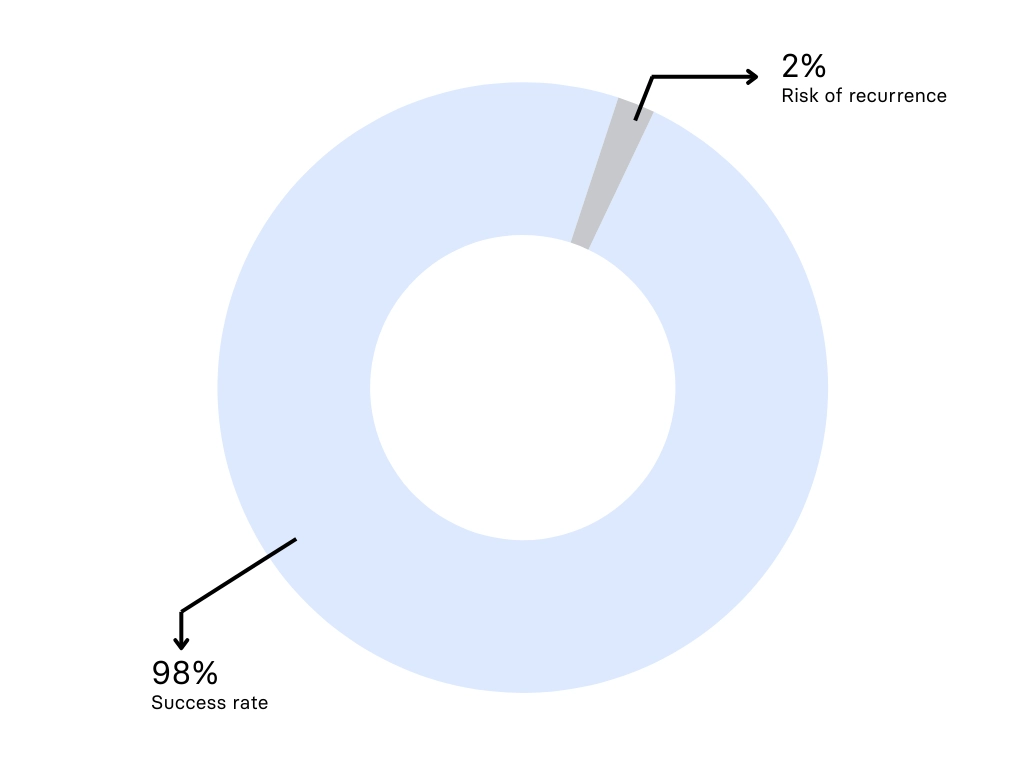
High success rate with minimal risk
Mesh repairs are often promoted as the gold standard due to concerns about high recurrence rates with non-mesh techniques. However, our experienced surgeons have refined the mesh-free approach to achieve a 98% success rate, with only a 2% risk of recurrence—virtually identical to the results of mesh-based repairs.
This means that using mesh offers no significant advantage over our specialised technique, while our approach avoids the risks associated with mesh implants, such as chronic pain, inflammation, and foreign body reactions.
What sets our techniques apart from conventional hernia surgery?
Your groin is a sensitive area crucial for movement, flexibility and sexual function. Hernias disrupt this balance, causing discomfort and affecting quality of life. Our mesh-free approach restores strength and function naturally, avoiding synthetic mesh implants for a safer recovery.
Repairing the root cause
Imagine a hernia as a hole in the tissues of your groin—a weak spot that allows tissue like fat or intestine to bulge through. Mesh-based operations place a synthetic patch over or under this hole, but they don’t fix the underlying weakness.
Our mesh-free technique addresses the source by closing the defect, restoring strength, and providing a durable solution without relying on synthetic materials.
A better fit for a dynamic area
The groin is a highly mobile part of your body, involved in everything from walking and bending to sexual activity. Unlike synthetic mesh, which remains rigid and can irritate surrounding nerves and tissues, a mesh-free repair uses your body’s natural flexibility to adapt and heal. This ensures that the repair integrates smoothly with your daily movements and doesn’t interfere with the sensitive structures in the area.
Avoiding unnecessary risks
Mesh repairs come with potential complications, especially in a sensitive area like the groin. Chronic pain, infections, or discomfort from having a foreign object in your body are all risks associated with synthetic mesh. By relying on your own tissue, our mesh-free technique eliminates these risks and promotes natural healing, so you can recover without added worry.
Step-by-step visuals
Follow the links below for a detailed, illustrated step-by-step guide for each of the two techniques we use for inguinal hernias.
The benefits of our mesh-free repairs
Inguinal hernia surgery without plastic mesh, reduces the risk of complications such as infection and chronic pain, promotes natural healing, and preserves the body’s integrity.

Avoid mesh-related complications
Like most of our patients, you may prefer a mesh-free hernia repair to avoid complications and support your long-term well-being by relying on your body’s own tissue for a more natural recovery.

Fits an active lifestyle
We prioritise preserving your abdomen’s natural flexibility and function by using your body’s own tissue for the repair, avoiding the risks and complications associated with plastic implants.

Experienced team
Our team of skilled surgeons, anesthetists, and nurses, trusted by top athletes, provide world-class mesh-free hernia surgery with the highest standard of care.

Personalised treatment
We take pride in offering personalised treatment plans that prioritise addressing your specific needs and tailoring your recovery every step of the way—from the initial consultation to post-operative care.

Fits an active lifestyle
We prioritise preserving your abdomen’s natural flexibility and function by using your body’s own tissues, avoiding unnecessary stress or complications by foreign body implants.

Avoid mesh-related complications

Experienced team
Our specialised team of surgeons, anesthetists, and nurses, who also treat top athletes, provide you with world-class, mesh-free hernia care.

Personalised treatment
Honest reviews from those who chose us

Steven Price
”I had a hernia operation through BioHernia with Dr Koch in Germany just four weeks ago. As I type I’ve had no problems, and no pain for several weeks…”

Gerard Thomas
”Top job Dr Weise! Had my doubts but highly recommended….”
”My experience with BioHernia and Dr. Andreas Koch (Surgeon) was brilliant. I am pleased with the results of the operation…”

John C.
”I am a very happy customer of BioHernia. They arranged a mesh-less hernia repair for me with Dr Wiese in Frankfurt….”

Michael Yiasemides
”I am very happy with all aspects of my inguinal hernia repair, performed by Dr Koch…..”

Ed O'Connor
”Great service from Dr. Koch and his team. The process was so easy from start to finish thanks to Biohernia. I have applied for reimbursement of the costs from the Health Service Executive in Ireland…”

Elaine Sivyer
”I chose Biohernia in Frankfurt for hernia surgery, as my inguinal hernia was small (but so painful!) and I wanted to avoid mesh. I’d been in severe pain for months in the UK, trying to make progress through the health system – but my life was falling apart as I was mostly bedridden….”

Neil Doyle
”First and foremost, Dr. Koch’s surgical skills were nothing short of exceptional. His expertise in inguinal hernia repair instilled confidence…”

Brian Shelton
”Best Decision: My mesh free operation to correct an inguinal hernia was performed on a Wednesday morning a short 6 weeks after my initial call to Biohernia….”

Daniel Sab
”The last words from Dr Wiese I remember before to fall asleep in the operatory room were “You are in safe hands…”

Rik Kav
”I decided to get my hernia repaired by a specialist, rather than a general surgeon, and also in Ireland there are no surgeons who don’t use mesh…..”

edddwick
”I flew from Ireland for my surgery, having done my research and following the advice of an acquaintance who had done the same…”

Kev B
”I am a 49 year old male from the UK and I had a right ingunial hernia. I was given the opportunity via Biohernia to have a non-mesh repair done by Dr Andreas Koch in Cottbus Germany. The operation was a great success…..”

Julien Vailles
”Overall, I had a VIP experience with a great result in July 2021, my hernia is gone and I have no pain. I live in Ireland, I had an inguinal hernia for over 2 years …”
How BioHernia works
Assessment and video consultation with our surgeon
Travelling to our clinic
Undergoing the procedure
Recovery at home
We set the bar for mesh-free hernia surgery — and keep raising it
As pioneers in mesh-free hernia surgery, we are dedicated to leading the way in innovative, patient-focused treatments. Over 25 years ago, our surgeons were among the first to challenge the widespread use of plastic meshes in hernia surgery. Their commitment to providing safer, more natural solutions has driven our mission ever since.
With decades of experience and countless successful operations, our surgeons, along with our entire team, have continuously refined and perfected our procedures, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care.
25+
years headstart in specialising and improving mesh-free hernia repair techniques
500+
operations done yearly by each of our surgeons, anesthesists and nurses
What our experience means for you:
Reduced recurrence rates
Introduction of lighter forms of anesthesia
Less recovery time
Preservering important muscles and nerves
Reduced incision size
Reduced operation risks
Reduced suture materials
Less operating time
Development of post-operative recovery plans for top mobility
Treatment in our clinics
Discover why thousands of people from around the world choose our clinics for treatment. Here, you’ll receive compassionate care, unmatched expertise, and exceptional skill, ensuring the best possible experience.
1 – Pre-operation
The day before your operation, you’ll visit the clinic for final pre-surgery checks. During this visit, you’ll meet your surgeon and anesthesiologist, who will walk you through the procedure and answer any remaining questions you may have.
Will the surgeon examine my hernia?
Yes, your surgeon will perform a full examination the day before your operation, taking time to answer any questions you may have. Additionally, the anesthesiologist will conduct tests to ensure you’re fully prepared for the procedure the next day.
What should I do to prepare for the operation?
Follow any instructions provided by your surgeon, such as fasting before the procedure or temporarily stopping certain medications. Stay hydrated the day before (unless instructed otherwise) and ensure you get a good night’s sleep. Arriving well-rested, relaxed, and on time will help ensure a smooth process. If you have any questions about preparation, don’t hesitate to reach out to our team.
2 – The operation
Our operations are typically scheduled in the morning and take about 90 minutes to complete. After the procedure, you’ll wake up gradually in the recovery room, where our team will monitor you closely. Once you’re feeling steady and comfortable, you’ll be able to leave the clinic on your own feet.
OPERATION DETAILS
Waiting list | Two weeks |
Duration of operation | 90 minutes |
When to stop eating before operation | Exact time will be instructed day before operation |
Type of anaesthetics | General anesthesia |
Type of incision | Open incision (5 cm) (on each side) |
Success rate | 98% (2% risk of recurrence) |
Length of scar after operation | Three to five centimeters (on each side) |
Time to walking | Directly after operation |
Time to driving car/cycling | Driving is allowed after one week |
Time to full recovery | Six weeks |
Time to cycling | Light cycling after one week |
Showering | One day after operation |
Wound care | Apply new wound dressing daily, for six days | No sutures to be removed |
Flying |
|
3 – After care
In the three days after your operation, you’ll have follow-up visits with your surgeon to support your recovery. These appointments allow your surgeon to monitor your healing, address any concerns, and provide personalised advice to ensure a smooth and successful recovery.
Looking for more information?
For a more in-depth look at each step of the process, from consultation to recovery, check out our comprehensive Patient guide. It’s designed to answer all your questions and help you feel fully prepared for your operation.
The science behind better hernia surgery
We believe in providing the best care by using techniques backed by solid research and proven results. Our mesh-free operation methods are supported by clinical studies, many of which are conducted by our own experienced surgeons.
The road to full recovery
After your hernia repair repair, the journey to full recovery begins. We’re committed to helping you navigate this road to healing, ensuring you can embrace your active lifestyle once again. In the first week you might experience a bit of discomfort at the operation site. It’s not unusual to notice some swelling or a touch of bruising. Best to take it easy this week, though a short stroll can help with blood flow and ease stiffness.
Avoid lifting anything heavier than 10kg to give your body the time it needs to heal properly.
Focus on fibre-rich foods to prevent constipation and include plenty of protein to support tissue repair.
Stay active with light movement like walking, as it promotes blood flow and supports recovery.
The following weeks
As you move into the second week and beyond, your recovery will gradually progress. Swelling and bruising should subside, and your energy levels will start to return. While it’s important to continue avoiding heavy lifting or intense activity, you can begin to reintroduce more of your usual routine during this period.

Weeks 2 and 3
You can slowly increase your activity level, incorporating light household tasks, short walks, or gentle cycling on a stationary bike at home or in the gym. These are all great ways to improve blood flow and rebuild strength without placing strain on the surgical site. Be sure to listen to your body and avoid pushing yourself too hard during this stage.

Weeks 6 and onwards
By this stage, your recovery is well underway, and you’ll feel significantly stronger. You can confidently return to your regular activities, including more dynamic exercises like running or competitive sports. For those who enjoy weightlifting or more strenuous workouts, this is the time to start reintroducing these activities. While the repair is strong enough to handle heavier lifting, it’s still important to ease into it, gradually increasing intensity to allow your body to fully adapt. Most patients find they’re back to feeling like themselves by the end of week 6, ready to embrace an active lifestyle without limitations.
Resuming normal life
1. When can I return to work?
Most patients can return to office work or light-duty tasks within 1–2 weeks. However, for physically demanding jobs, it’s best to wait until 6 weeks after the procedure.
2. When can I start exercising again?
You can resume light activities, such as walking, within the first week after surgery. For more strenuous exercises like weightlifting, running, or intense workouts, it’s best to wait 6 weeks and ease back into them gradually, paying close attention to how your body feels.
3. Will I have any permanent restrictions?
No, after the recovery period, you’ll be able to return to your previous activity and fitness levels without any limitations. Whether it’s working out, heavy lifting, or enjoying your favorite hobbies, you can confidently resume life as it was before the hernia—strong, active, and unrestricted.
Hear from people that chose BioHernia
Life-Changing Experience
“I was anxious about traveling for surgery, but everything was handled so well. Dr. Koch even checked on me at the hotel daily after the operation. While staying there, I met a few Dutch patients who were also having the procedure. We ended up chatting a lot, sharing recovery tips, and even formed some friendships along the way. It really helped make the whole experience feel less overwhelming.”
John, 54
Quick recovery and back to work
“I was worried about taking too much time off from work, but they were right about the four-week recovery. To be honest, I started feeling like myself again even sooner than I expected.”
Abdul, 37
Great experience with Dr. Wiese
“I traveled to Frankfurt for my hernia repair at Dr. Wiese’s clinic, and it was well worth it. From the pre-op discussions to post-op care, everything was organised perfectly. Dr. Wiese’s light-hearted humor really helped put me at ease before surgery, making the whole experience much less stressful.”
Thomas, 49
Exceptional Care and Fast Results
“I chose BioHernia because I wanted to avoid mesh, and the Shouldice repair was perfect for me. The surgery went smoothly, and the team at the clinic in Cottbus was incredibly attentive. The follow-up care at the hotel, where Dr. Koch visited me daily, gave me peace of mind. Recovery was a bit longer, but so worth it for a mesh-free solution.”
Paul, 67
Quick recovery and minimal pain
“After my bilateral hernia repair, I stayed in a nearby hotel where Dr. Koch visited to check on my progress. I was walking the day after surgery and had only minor discomfort. Two weeks later, I was back to light exercise, and by six weeks, fully recovered!”
Dave, 28
Frequently asked questions
Can an inguinal hernia heal on its own?
No, an inguinal hernia cannot heal on its own. Without treatment, a hernia can worsen over time, leading to complications such as pain, increased swelling, or even strangulation, where the blood supply to the affected tissue is cut off, and you have to undergo emergency surgery.
What causes an inguinal hernia?
An inguinal hernia occurs when tissue, such as part of the intestine, protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles. Several factors can contribute to the development of this condition, including:
- Physical Strain: Heavy lifting, straining during bowel movements, or persistent coughing can put extra pressure on the abdominal muscles, leading to an inguinal hernia.
- Weak Abdominal Wall: Some people are born with a naturally weak abdominal wall, making them more susceptible to hernias.
- Aging: As we age, our muscles tend to weaken, which can increase the risk of developing a hernia.
- Previous Surgery: Operations in the abdominal area can weaken the muscle wall, making hernias more likely.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions that increase pressure in the abdomen, such as obesity or fluid buildup, can contribute to hernia development.
Can I exercise with an inguinal hernia?
Yes, but if you have an inguinal hernia, it’s crucial to be cautious with physical activity. While light exercises, such as walking or gentle stretching, are generally safe, activities that involve heavy lifting, intense straining, or high-impact movements should be avoided as they can worsen the hernia.
Are operations done under general or local anesthetic?
Because bilateral hernia surgery is more complex than a one-sided repair, we only perform it under general anesthesia. This ensures your comfort and allows the surgeon to complete both sides with the highest precision and care.
Do the surgeons always perform the operations themselves?
Yes, at our clinic, our highly experienced surgeons personally perform all operations to ensure the highest standards of care. They are directly involved in every step of the procedure, from the initial consultation to the surgery itself, and the post-operative follow-up.
When can I travel back home?
You can usually travel back home hree to four days after the operation. This allows enough time for initial recovery and for your surgeon to ensure there are no immediate complications. Your surgeon will give you specific guidance based on how you’re feeling post-surgery.
Is bilateral hernia surgery more complicated than single-sided surgery?
Bilateral hernia surgery is slightly more complex as it involves repairing hernias on both sides. However, our experienced surgeons perform both repairs during the same operation with precision and care, ensuring the same high standards are applied to both sides.
Will recovery take longer after bilateral hernia surgery?
Yes, recovery from bilateral hernia surgery typically takes slightly longer, around 6 weeks, as the body needs to heal on both sides simultaneously. Additionally, you won’t have a “healthy side” to rely on during recovery, which can make daily tasks like getting out of bed or sitting down more challenging. However, after the full recovery period, you can return to your normal, active lifestyle without any limitations.

